MambaRALM: Analyzing RALMs with Selective State Space and Transformer Based Architectures for Long Sequence Modeling
Abstract
This study examines the efficacy of Retrieval Augmented Language Models (RALMs), a recent paradigm incorporating retrievers to enhance standalone language models during inference. While most RALMs rely on transformer architecture, which suffers from scalability issues limiting context windows, this project explores the potential of the Mamba architecture, known for its proficiency with long sequences and Long Range Dependencies (LRDs), in improving RALMs’ performance. The study constructs a RALM based on the Mamba architecture and evaluates it alongside a transformer-based RALM on a subset of the TriviaQA dataset. Results show comparable performance for small to medium context chunks ($k \leq 7$), but the Mamba-based RALM demonstrates better resilience to larger context sizes ($k > 7$), indicating its potential for handling irrelevant information more effectively.
SSMs
Structured State Space Models (SSMs) are a class of models that represent dynamic systems using state variables and structured matrices to capture temporal dependencies. This class of models is based on control theory, which provides the concept of using state-space representations to model and analyze dynamic systems over time.
I have detailed notes on the papers Efficiently Modeling Long Sequences with Structured State Spaces (also called S4) and How to Train Your HiPPO: State Space Models with Generalized Orthogonal Basis Projections by Albert Gu et al which form a solid foundation for state space models for deep learning. You can view my notes on S4 here and a general overview of S4 and How to Train your HiPPO here.
Mamba
The Mamba architecture is an extension on the S4 architecture created by Albert Gu which tends to outperform Transformer architectures on similar tasks, especially for long sequence modeling.
Transformer
The Transformer is a deep learning model architecture designed for handling sequential data, using self-attention mechanisms to process input data.
Transformers are well known due to the profound success of modern Large Language Models (LLMs) that utilize Transformers.
RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a method that combines information retrieval and generative models to enhance the quality of generated responses by retrieving relevant external knowledge before generating text.
RAG often uses vector databases, where the vectors are sentence embeddings from models like BERT, to perform fast similarity search and retrieval to augment prompts for LLMs.
Retreival Augmented Language Models (RALMs) are LLMs that have been augmented with RAG.
We used this project to study the performances of Transformer and Mamba in long sequence modeling specifically for RALMs. We did this by measuring performance of each RALM as the number of retrieved chunks, \(k\), from the vector database grew.
Manuscript and Code
RAG and Model Comparison Pipeline
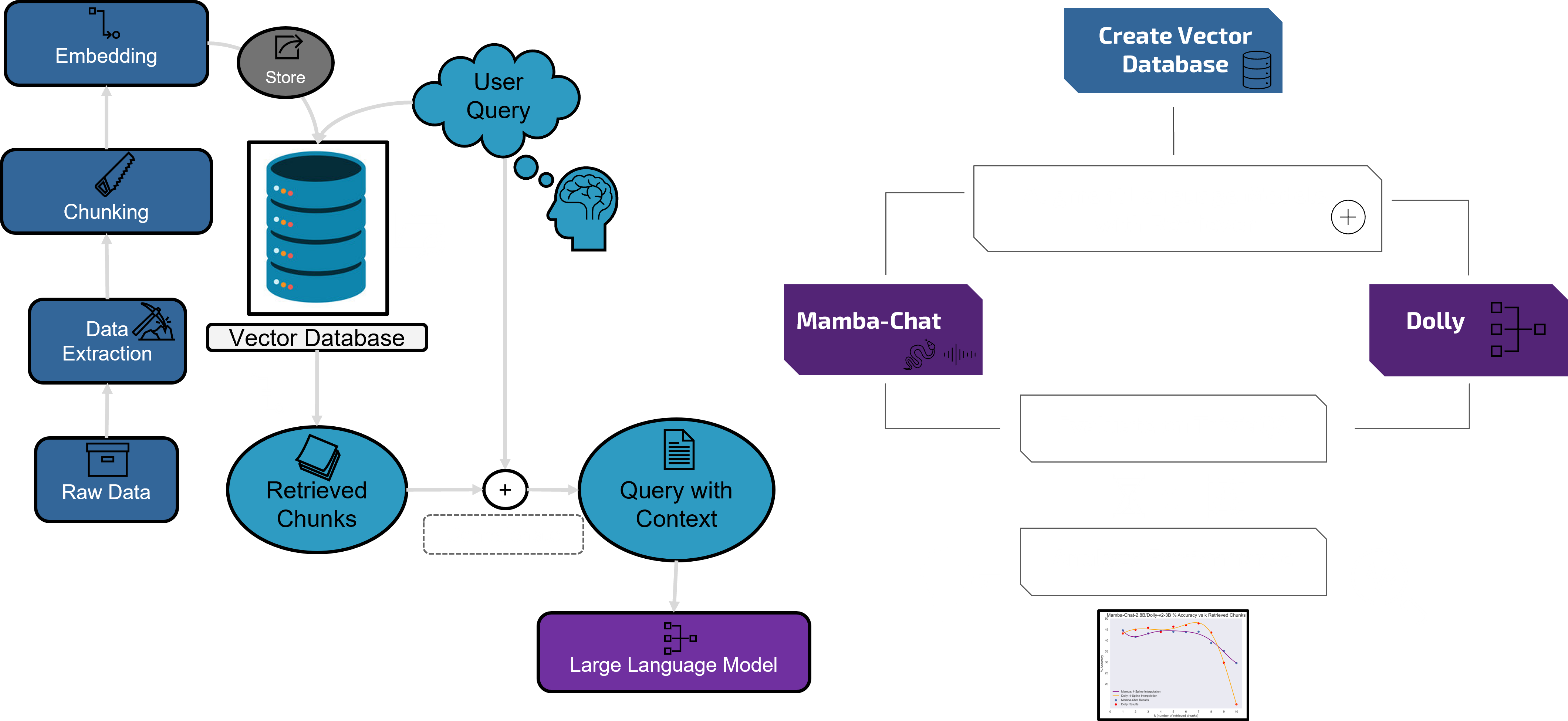 Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Model Comparison (Mamba vs. Transformer) Processing Pipelines
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Model Comparison (Mamba vs. Transformer) Processing Pipelines
